Quick Contact

IEC 62304 Standard
IEC 62304 standard applies to the entire software life cycle, including software development, verification, validation, and maintenance processes. It covers software used in medical devices, including embedded software, firmware, and software that is part of a medical device / standalone software (SaMD).
It is an international standard that specifies requirements for the life cycle processes of medical device software. It guides the development, maintenance, and risk management of software used in medical devices.
IEC 62304 standard acknowledged by regulatory bodies across the globe, such as the US FDA and the EU (MDR and IVDR) as a dependable foundation for the creation of secure and efficient medical device software. Developers can streamline the process of gaining regulatory approvals by aligning their processes with established industry standards by conforming to their requirements.

(Listen for 6 Minutes)
IEC 62304 Software Classification
IEC 62304 standard establishes a cohesive framework for designing and testing software for medical devices through defined processes, activities, and tasks, ensuring safe usage in patients. The standard categorizes software into three safety classes according to the risk to the patient from a possible software failure
- Class A: No injury or damage to health is possible
- Class B: Non-serious injury is possible
- Class C: Death or serious injury is possible
IEC 62304 Implementation
The subsequent 5 chapters of IEC 62304 detail specific requirements and guidelines for the development and proper implementation of medical device software.
| Chapter | Description |
|---|---|
| Chapter 5 | Software development and planning process including requirements analysis, design, testing, and release processes. |
| Chapter 6 | Software maintenance plan, including the implementation of a maintenance plan and issue analysis procedures. |
| Chapter 7 | Software risk management and identification of hazardous situations, risk control, verification, and risk management procedures following the ISO 14971 standard. |
| Chapter 8 | Software configuration management including change control and configuration status tracking. |
| Chapter 9 | Software problem resolution investigating and reporting on problems, change control processes, trend analysis, and resolution testing and verification. |
The FDA encourages the use of recognized consensus standards to show compliance. IEC 62304 standard acknowledged by the FDA for this purpose. Employing 62304 can facilitate the 510k submission process as it offers a comprehensive framework for software development, risk management, and documentation.
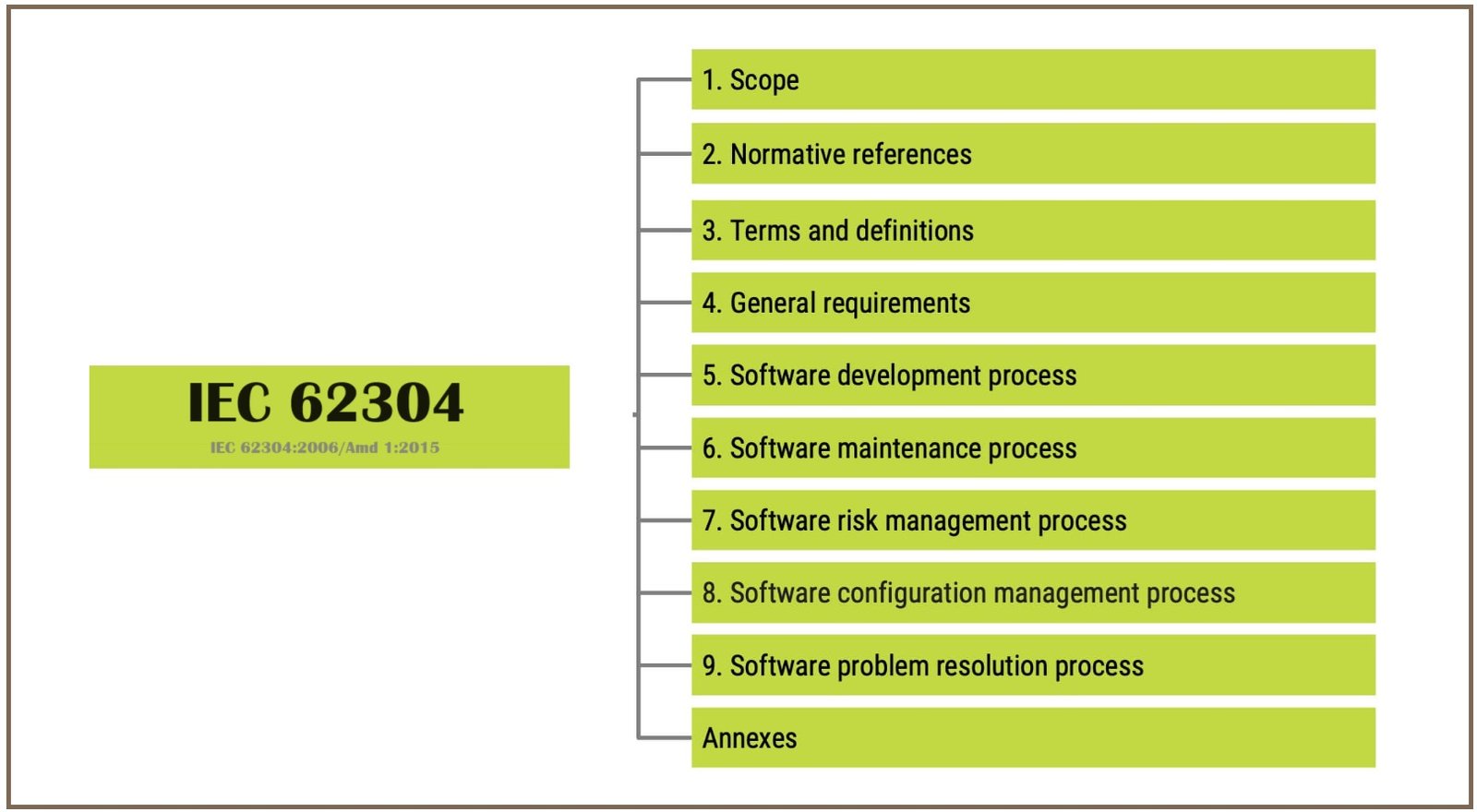
IEC 62304 Consultants
IEC 62304 Consultants play a vital role in guiding organisations through the process of complying with the standard’s requirements and implementing best practices for medical device standard compliance. Here’s a breakdown of their key roles:
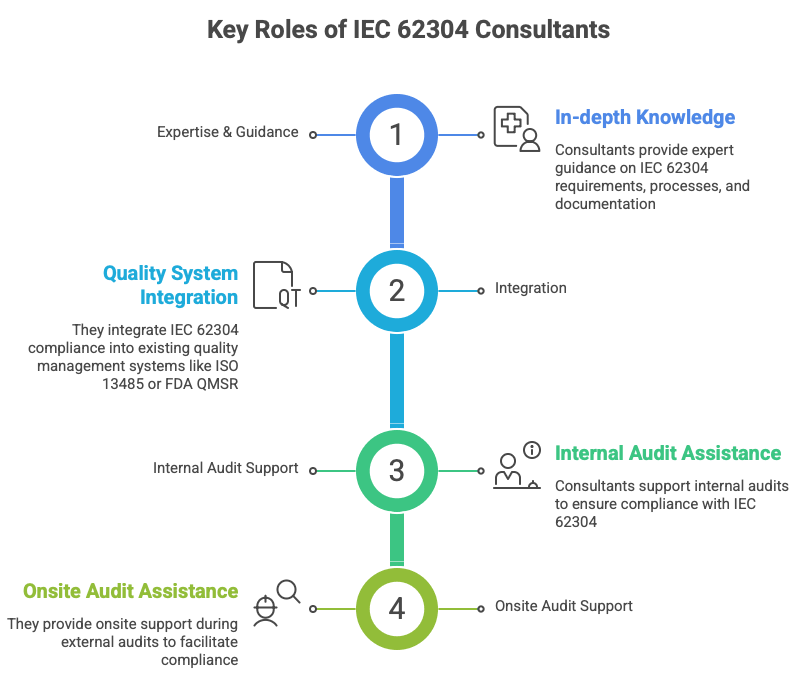
Effectively coordinating with consultant team with software developers requires careful planning, clear communication, and a focus on building relationships and trust. By implementing the strategies outlined in this document, organizations can leverage the expertise of consultants to achieve their project goals while ensuring knowledge transfer and long-term sustainability. Remember that flexibility and adaptability are key to success when working with consultant teams. Continuously evaluate and refine your coordination strategies to optimize performance and achieve desired outcomes.
Benefits of Implementing IEC 62304 Standard
Implementing the IEC 62304 standard offers several benefits for software medical device manufacturers (SAMD & SIMD). A few are listed below:
- Compliance with 62304 helps ensure that medical device software is developed with patient safety as a primary consideration. By identifying and mitigating risks throughout the software lifecycle, organizations can minimize the likelihood of software-related errors or malfunctions that could harm patients
- Adhering to 62304 facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements in the European Union, the United States, and other regions where the standard is recognized. This can streamline the regulatory approval process and expedite certifications and approvals faster
- The standard emphasizes the importance of risk management in medical software. By systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, organizations can proactively address potential hazards and ensure the safety and effectiveness of their final released software
IEC 62304 Standard Requirements
IEC 62304 is a standard that outlines requirements and guidelines for the development of medical device software; however, it does not ask for a certification or no certification body issues certificates. Organizations can demonstrate compliance with 62304 by implementing the standard’s requirements and following its guidelines throughout their software development processes
While there is no formal IEC 62304 Standard, organizations can still provide evidence of their adherence to the standard through documentation and audit reports. This can help build confidence in customers, regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders
With the help of IEC 62304 consultants such as I3CGlobal, the developers can identify, prepare, modify, implement, and conduct regular reviews and updates to these procedures to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness in managing software development activities.
List of IEC 62304:2006 Procedures
Compliance with IEC 62304 is a mandatory requirement for FDA 510k and the EU MDR /IVDR CE Marking technical documentation. Developing procedures compliant with 62304 requires a systematic approach to software development, verification, validation, and maintenance. These procedures should be prepared to the specific needs and context of your organization and should be documented, implemented, and maintained based on a medical device quality management system platform such as ISO 13485 OR 21 CFR 820 or FDA QMSR. The below list provides procedure requirements against each class.
| No | CL# | Procedure Name | Requirement | Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.1 | Software Development Planning | Establish software development plans appropriate to scope, magnitude and safety classification. | A+B+C * | ||
| 2 | 5.2 | Software Requirements Analysis | Define and document SOFTWARE SYSTEM requirements from system-level requirements. | A+B+C | ||
| 3 | 5.3 | Software Architectural Design | Transform requirements into architecture, define interfaces, specify SOUP requirements, identify risk controls, and verify architecture. | B+C * | ||
| 4 | 5.4 | Software Detailed Design | Refine architecture, develop detailed design, define interfaces, and verify design. | B+C *** | ||
| 5 | 5.5 | Verification of Software Unit | Establish strategies, methods, and procedures for verifying each software unit. | A+B+C **** | ||
| 6 | 5.6 | Verification & Testing of Integrated Software | Verify software integration and test integrated software items as per integration plan. | B+C | ||
| 7 | 5.7.1 | Software System Testing | Establish and perform system tests covering all software requirements. | B+C | ||
| 8 | 5.7.3 | Retest After Changes | Retest the software system when changes occur during testing. | B+C | ||
| 9 | 5.8 | Software Release | Ensure all lifecycle activities and documentation are complete before release. | A+B+C ***** | ||
| 10 | 6.1 | Establishing Software Maintenance Plan | Establish software maintenance plans for lifecycle maintenance activities. | A+B+C | ||
| 11 | 6.2.1 | Feedback | Monitor feedback from internal sources and users on released software products. | A+B+C | ||
| 12 | 6.2.3 6.2.4 6.2.5 |
Analysis, Approval & Communication of Changes | Analyse and approve change requests and communicate changes to users and regulators. | A+B+C ****** | ||
| 13 | 6.5 | Implementation of Approved Modifications | Implement approved modifications using development or maintenance processes. | A+B+C | ||
| 14 | 7 | Risk Management Process | Risk management activities performed in accordance with ISO 13485. | A+B+C ******* | ||
| 15 | 8 | Configuration Management | Establish configuration identification and version control for software items. | A+B+C | ||
| 16 | 9 | Software Problem Resolution | Record, investigate, analyse, resolve, and trend software problems. | A+B+C | ||
| Note |
|---|
| * Clause 5.1.4 applies only to Class C; Clauses 5.1.5, 5.1.10 & 5.1.11 apply only to Class B & C |
| ** Clause 5.3.5 applies only to Class C |
| *** Clauses 5.4.2, 5.4.3 & 5.4.4 apply only to Class C |
| **** Clauses 5.5.2, 5.5.3 & 5.5.5 apply only to Class B & C; Clause 5.5.4 applies only to Class C |
| ***** Clauses 5.8.1 to 5.8.8 apply only to Class B & C |
| ****** Clause 6.2.3 applies only to Class B & C |
| ******* Clause applicable for Class A in Section 7 is 7.4.1 |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is medical device software?
Any software associated with a medical device or Invitro diagnostic device regardless of software in a medical device, software as a medical device, firmware, or embedded software is called medical software.
What Types of Software are Included?
Software used for medical device design, development, production, installation, and support is covered under the IEC 62304 standard. This includes the supporting software used in production and quality control in addition to the software that works directly with the patient or performs a medical function.
What is the timeline for ISO 62304 Implementation?
ISO 62304 Implementation generally, it takes 3-4 months.