IVDR Classification
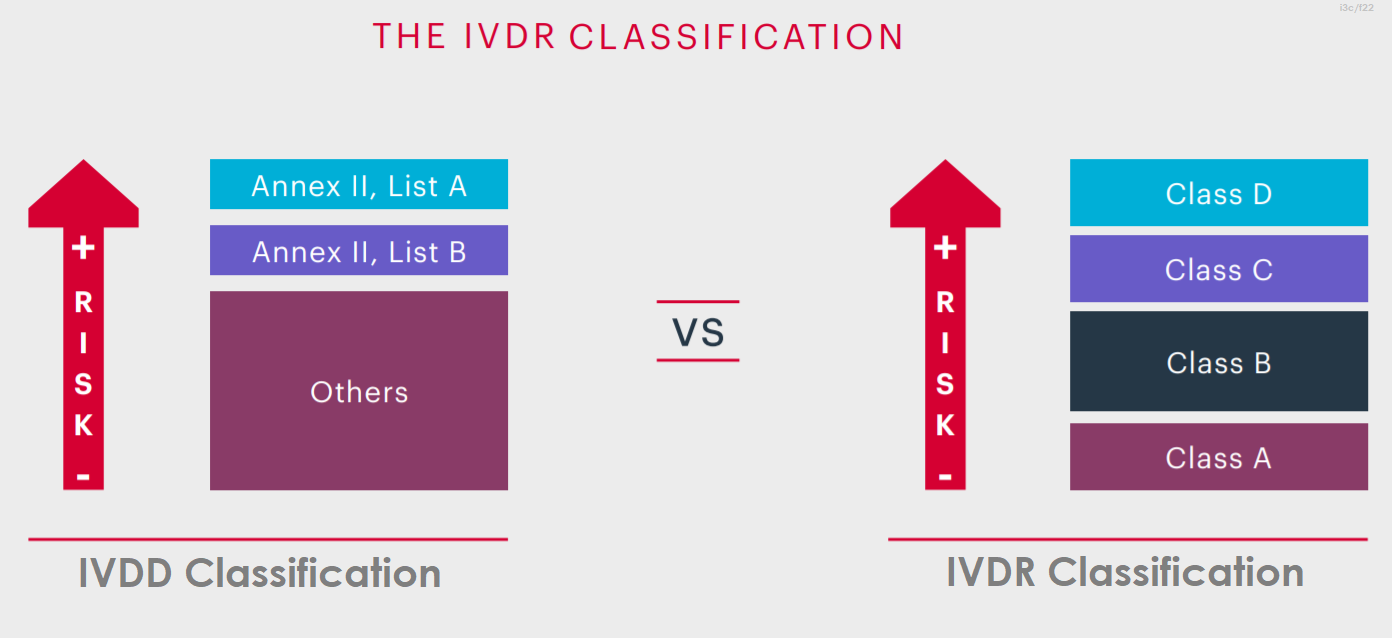
Manufacturers must classify their in vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices by the rules outlined in Annex VIII of Regulation (EU) 2017/746, commonly referred to as IVDR classification. The IVDR classification is based on the intended purpose and inherent risks, therefore they are classified A, B, C and D considering their intended purpose and inherent risks.
How IVDR are classified?
IVDR classified as A, B, C and D considering their intended purpose and their inherent risks. The lowest risk category at Class A, up to the highest at Class D.
The new system for classifying IVD medical devices represents a significant departure from the current IVD directive, constituting one of the few radical changes introduced by the new regulations. It represents an enhancement over the existing directive, aligning the classification of IVD medical devices with that of other devices and adhering to international practices advocated by the GHTF. Moreover, it offers a more comprehensive approach compared to the current directive, facilitating a smoother application to new IVD devices.
♦ Instruments,
♦ Specimen receptacles,
♦ Wash buffers
♦ etc.
As per EU IVDR Classification for Class A devices (Excluding Sterile), Medical device CE marking could be achieved through EU Declaration of Conformity [Annex III].
♦ Thyroid function tests,
♦ Infertility assays,
♦ Clinical Chemistry
♦ etc.
As per EU IVDR Classification for Class B devices, CE marking for medical devices could be achieved through below conformity assessment route
♦ Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX] followed by Assessment of Technical Documentation per category device [Annex IX 4.4-4.8].
♦ Genetic tests,
♦ Companion diagnostics,
♦ Blood gas analysers,
♦ Caner markers,
♦ Rubella,
♦ Neonatal screening for metabolic disorders
As per EU IVDR Classification for Class C devices, CE marking could be achieved through the any of the below conformity assessment routes
♦ Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX] followed by Assessment of Technical Documentation per generic device [Annex IX 4.4-4.8] followed by For Companion Diagnostics Competent Authority consultation [Annex IX 5.2]
♦ Type Examination [Annex X] (includes Technical Documentation) followed by Production Quality Assurance [Annex XI] followed by For Companion Diagnostics Competent Authority consultation [Annex X 3]
Class D for high personal risk, high public health risk device. Few examples are below.
♦ Blood grouping ABO
♦ Rhesus (including RHW1)
♦ Kell
♦ Kidd and Duffy systems
♦ Syphilis (used for screening of blood donations)
♦ Hepatitis B and C
As per EU IVDR Classification for Class D devices, CE marking could be achieved through the any of the below conformity assessment routes
♦ Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX] followed by assessment of Technical Documentation [Annex IX Ch II] followed by Verification by EU Reference Laboratory
♦ Type Examination [Annex X] (includes Technical Documentation) followed by Production Quality Assurance [Annex XI] followed by Verification by EU Reference Laboratory
Do you need an email containing full details about IVDR Classification within 2 minutes? Share your email below: Privacy Policy>>
IVDR Classification Rules
The responsibility for identifying the applicable risk class of its IVD device lies with the manufacturer. However, for Classes B, C, and D devices, the notified body will verify the accuracy of this classification. Additionally, competent authorities may also verify the classification, including for Class A devices. Therefore, manufacturers must maintain a documented rationale for their classification decisions in the IVDR Technical documentation.
Examine all IVDR classification rules below thoroughly and ascertain which rule corresponds to the highest risk class applicable to the device. It’s conceivable that multiple rules may be relevant or that the device serves various intended uses. In such instances, the rule leading to the highest risk class must be applied.
Rule 1
This rule applicable for most of the devices in Class D,
(a) determination of infectious load of a life-threatening disease,
(b) transmissible agent in blood, cells, tissues or organs and blood components.
Rule 2
This rule applicable for most of the devices majorly in Class C and few in Class D
Devices intended to be used for blood grouping, or tissue typing to ensure the immunological compatibility of blood, blood components, cells, tissue or organs that are intended for transfusion or transplantation or cell administration.
Rule 3
Generally majority of the IVD devices falls under this category are in Class C
Device used for (a) sexually transmitted disease (b) foetus or embryo (c) pre-natal screening of women (d) infective disease status or immune status (e) screening, diagnosis, or staging of cancer (f) human genetic testing (g) screening for congenital disorders in the embryo or foetus (h) congenital disorders in new-born babies etc.
Rule 4
Majority of the Devices falls under Class C and few in Class B Intended for self-testing
Note : exemption from devices for the detection of pregnancy, for fertility testing, Cholesterol / Glucose / Erythrocytes / Leucocytes / virus/ bacteria/ urine level determination.
Rule 5
Generally Class A devices falls under this rule.
General laboratory use accessories such as buffer solutions, washing solutions, culture media, histological stains used in IVD procedures and also some instruments for In Vitro procedures and specimen receptacles.
Rule 6
Class B Devices are not covered in any above EU IVDR classification (1-5) rules
Rule 7
Generally considered in Class B Devices
Devices which are controls without a quantitative or qualitative assigned value.
Support from experienced IVDR Consultants is essential, even if the employees are experienced with IVDD
Frequently Asked Questions
Do we need to maintain technical file for class A devices?
Does class A device exempt from NB CE Certification?
Very useful for small and medium size medical device manufactures


